В процессе создания кластера стал вопрос: чем же можно обеспечить синхронизацию файлов и папок на отдельных узлах? После недолгих поисков всевозможных готовых решений наткнулся на известную утилиту, работающую под Unix – Rsync. У многих администраторов появилась необходимость синхронизировать каталоги между Unix-Windows серверами. Так получил жизнь проект cwRsynс. Суть этого проекта в том, что утилита Rsync запускается по Windows с помощью библиотеки cygwin.
В моем случае возможность взаимодействия с Unix серверами в перспективе очень радовала. Также отзывы админов о работе Rsync под Unix были очень положительными, и я решил попробовать.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим каким образом настраивается синхронизация жесткого диска с помощью cwRsynс. Русскоязычных статей по работе с cwRsync я не нашел – все дружно копируют четыре шага по установке, и не касаются работы и настройки. Основную массу информации я черпал из http://rsync.samba.org, ведь параметры запуска для Rsync и cwRsync остаются одинаковыми.
Принцип синхронизации с помощью cwRsync состоит в следующем: на главном сервере (в нашем случае Сервер№1) запускается демон cwRsync при старте системы. В конфиге указывается к каким ресурсам будет даваться доступ. Клиент конфигурируется на втором сервере (Сервер№2). С определенной периодичностью на втором сервере запускается клиент, который соединяется с сокетом первого сервера, после чего происходит синхронизация. Взаимодействие происходит по локальным IP адресам:
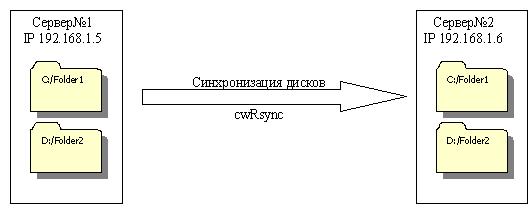
1. Установка cwRsync.
Для начала необходимо скачать и установить утилиту cwRsync. Установщик можно скачать отсюда.
Нужно выбрать последнюю версию. Перед установкой стоит убедиться, что совместима с конфигами старой версии.
Нам необходимо установить его на все узлы кластера. Процесс установки совсем прост: все значения можно оставить по умолчанию. cwRsync установиться в c:\Program Files\cwRsync\.
После установки можно выполнить следующие рекомендации:
Панель управления -> Система -> Дополнительно -> Переменные окружения
• Решите проблему с не-ascii символами. Т.е. нужно с www.okisoft.co.jp/esc/utf8-cygwin/ скачать файл cygwin.dll и заменить им тот, что идет в комплекте с cwRsync.
• Для того чтобы файлы с не-ascii смволами в имене нормально передавались, добавте —iconv=. в опции при вызове rsync.
У меня после установки проблем с кодировкой либо работой не наблюдалось. Также далее при конфигурировании я использовал прямые пути. Поэтому рекомендации можно не выполнять.
2. Работа с cwRsync на Сервер№1:
Для начала необходимо создать конфиг. файл. Создадим в c:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\ папки conf и log. В папке conf создадим файл rsyncd.conf следующего содержания:
#### rsyncd.conf file ####
uid = user_id
gid = user_id
use chroot = false # Даём разрешение использовать все диски а не только C. Если мы
# установим в true, то rsync сможет обращатся только к диску С.
hosts allow = 192.168.1.6 # Разрешаем обращаться только с Сервер№2
[drive_c] # Метка диска С
path = /cygdrive/c/
comment = this is system drive
read only = true
[drive_d] #Метка диска Д
path = /cygdrive/d/
comment = this is date drive
read only = true
#transfer logging = yes
#### End of configuration file ####
use chroot = yes – запуск rsync в chroot, для пущей безопасности;
[drive_с] – название модуля;
uid – должен соответствовать id владельца каталога, в который мы собираемся записывать;
path – полный путь до каталога, в который будем записывать;
list = no – не показывать секцию [push] в листинге;
comment – комментарий;
read only = false – открыть секцию на запись;
hosts allow – разрешить доступ к секции push только для определённых адресов;
auth users = push – разрешить доступ только пользователю push;
secrets file – файл соответствия имени пользователя определённому паролю.
Примечание:
2009/01/06 13:27:35 [3748] name lookup failed for 127.0.0.1: Unknown server error 2009/01/06 13:27:35 [3748] connect from UNKNOWN (127.0.0.1) 2009/01/06 13:27:35 [3748] rsync: chdir / failed : No such file or directory (2)
Зато когда указываешь имя папки в параметрах клиента, то всё работает.
Далее создадим bat файлы для запуска демона: создадим в папке conf файл rsync_server_start.bat с таким содержимым:
"C:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\rsync.exe" --config "C:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\conf\rsyncd.conf" --daemon --log-file "C:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\log\rsyncservice.log" --address 192.168.1.5
--config rsyncd.conf – указываем, где находится файл конфигурации. --daemon – запуск демона --log-file – включение ведения лога --address – указываем , какой адрес слушать
Полный перечень возможных параметров:
--daemon run as an rsync daemon
--address=ADDRESS bind to the specified address
--bwlimit=KBPS limit I/O bandwidth; KBytes per second
--config=FILE specify alternate rsyncd.conf file
--no-detach do not detach from the parent
--port=PORT listen on alternate port number
--log-file=FILE override the "log file" setting
--log-file-format=FMT override the "log format" setting
--sockopts=OPTIONS specify custom TCP options
-v, --verbose increase verbosity
-4, --ipv4 prefer IPv4
-6, --ipv6 prefer IPv6
-h, --help show this help (if used after --daemon)
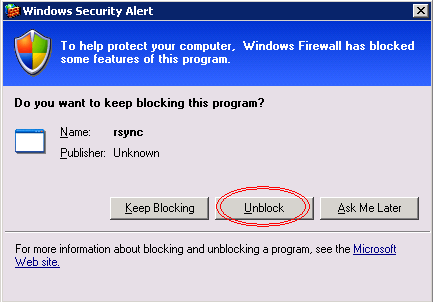
После запуска демона появится окно Windows Firewall и процесс в менеджере задач.
Windows Firewall: Блокирование rsync демона.
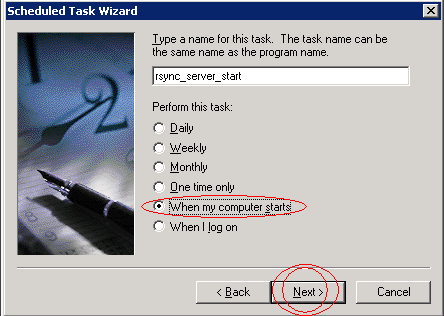
Необходима нажать Unblock. Если всё работает нормально, то нужно добавить запуск bat файла в Планировщик Задач:
Планировщик задач: Запуск демона cwRsync при старте сервера.
Таким образом, сервер cwRsync будет запускаться при старте узла.
3. Работа с cwRsync на Сервер№2:
Установим cwRsync на Сервер№2. Создадим в c:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\ папки bat и log. В папке bat создадим следующий файл с именем sync_all.bat. В этом файле создадим записи для синхронизации каждой необходимой папки. Следует включать исключения для папок с логами и статистикой. Вот общий вид строки.
"C:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\rsync.exe" -av --delete --exclude '/logs/' [email protected]::drive_c/Folder1/ "/cygdrive/c/Folder1/">"C:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\log\Folder1.log"
Необходимо сформировать подобные строки для каждой папки, и указывать их одна за одной в этом файле.
Примечание:
Каждая запись состоит из следующих частей
-a равносильно –rlptgoD r — рекурсивный режим l — пересоздание symlinks, это значит, что символические ссылки будут так же переноситься p – перенос прав t — передача времени модификации и его обновление на удаленной системе. Этот ключ должен быть установлен для точной синхронизации g — установить группу конечного файла таким же, как и у исходного o — установить владельца конечного файла таким же, как и у исходного v — verbose. Вывод сообщений в терминал. --delete - удаляет файлы, которых нет в источнике. --exclude – указываем то, что синхронизировать не нужно. user_id – uid, описанный на сервере @192.168.1.5 – IP адрес сервера ::drive_d /Folder_sync1/ – Метка сервера и путь "/cygdrive/d/Folder_sync1/" - куда >"C:\Program Files\cwRsync\bin\log\Folder_sync1.log" - весь вывод в файл
Обратите внимание на последний слеши в путях, так как они имеют значение для rsync. Если на конце исходной директории стоит «/», то это означает копирование содержимого директории; отсутствие слеша означает копирование директории и ее содержимого.
Если не указать /, то на клиент в папке создастся папка с файлами. Иначе просто её содержимое.
При первом запуске синхронизации на Cервер№2, также появится сообщения от брандмауэра Windows о блокировании Rsync. Необходимо нажать Unblock.
Вот список всех допустимых параметров:
-v, --verbose increase verbosity
-q, --quiet suppress non-error messages
--no-motd suppress daemon-mode MOTD (see caveat)
-c, --checksum skip based on checksum, not mod-time & size
-a, --archive archive mode; equals -rlptgoD (no -H,-A,-X)
--no-OPTION turn off an implied OPTION (e.g. --no-D)
-r, --recursive recurse into directories
-R, --relative use relative path names
--no-implied-dirs don't send implied dirs with --relative
-b, --backup make backups (see --suffix & --backup-dir)
--backup-dir=DIR make backups into hierarchy based in DIR
--suffix=SUFFIX backup suffix (default ~ w/o --backup-dir)
-u, --update skip files that are newer on the receiver
--inplace update destination files in-place
--append append data onto shorter files
--append-verify --append w/old data in file checksum
-d, --dirs transfer directories without recursing
-l, --links copy symlinks as symlinks
-L, --copy-links transform symlink into referent file/dir
--copy-unsafe-links only "unsafe" symlinks are transformed
--safe-links ignore symlinks that point outside the tree
-k, --copy-dirlinks transform symlink to dir into referent dir
-K, --keep-dirlinks treat symlinked dir on receiver as dir
-H, --hard-links preserve hard links
-p, --perms preserve permissions
-E, --executability preserve executability
--chmod=CHMOD affect file and/or directory permissions
-A, --acls preserve ACLs (implies -p)
-X, --xattrs preserve extended attributes
-o, --owner preserve owner (super-user only)
-g, --group preserve group
--devices preserve device files (super-user only)
--specials preserve special files
-D same as --devices --specials
-t, --times preserve modification times
-O, --omit-dir-times omit directories from --times
--super receiver attempts super-user activities
--fake-super store/recover privileged attrs using xattrs
-S, --sparse handle sparse files efficiently
-n, --dry-run perform a trial run with no changes made
-W, --whole-file copy files whole (w/o delta-xfer algorithm)
-x, --one-file-system don't cross filesystem boundaries
-B, --block-size=SIZE force a fixed checksum block-size
-e, --rsh=COMMAND specify the remote shell to use
--rsync-path=PROGRAM specify the rsync to run on remote machine
--existing skip creating new files on receiver
--ignore-existing skip updating files that exist on receiver
--remove-source-files sender removes synchronized files (non-dir)
--del an alias for --delete-during
--delete delete extraneous files from dest dirs
--delete-before receiver deletes before transfer (default)
--delete-during receiver deletes during xfer, not before
--delete-delay find deletions during, delete after
--delete-after receiver deletes after transfer, not before
--delete-excluded also delete excluded files from dest dirs
--ignore-errors delete even if there are I/O errors
--force force deletion of dirs even if not empty
--max-delete=NUM don't delete more than NUM files
--max-size=SIZE don't transfer any file larger than SIZE
--min-size=SIZE don't transfer any file smaller than SIZE
--partial keep partially transferred files
--partial-dir=DIR put a partially transferred file into DIR
--delay-updates put all updated files into place at end
-m, --prune-empty-dirs prune empty directory chains from file-list
--numeric-ids don't map uid/gid values by user/group name
--timeout=SECONDS set I/O timeout in seconds
--contimeout=SECONDS set daemon connection timeout in seconds
-I, --ignore-times don't skip files that match size and time
--size-only skip files that match in size
--modify-window=NUM compare mod-times with reduced accuracy
-T, --temp-dir=DIR create temporary files in directory DIR
-y, --fuzzy find similar file for basis if no dest file
--compare-dest=DIR also compare received files relative to DIR
--copy-dest=DIR ... and include copies of unchanged files
--link-dest=DIR hardlink to files in DIR when unchanged
-z, --compress compress file data during the transfer
--compress-level=NUM explicitly set compression level
--skip-compress=LIST skip compressing files with suffix in LIST
-C, --cvs-exclude auto-ignore files in the same way CVS does
-f, --filter=RULE add a file-filtering RULE
-F same as --filter='dir-merge /.rsync-filter'
repeated: --filter='- .rsync-filter'
--exclude=PATTERN exclude files matching PATTERN
--exclude-from=FILE read exclude patterns from FILE
--include=PATTERN don't exclude files matching PATTERN
--include-from=FILE read include patterns from FILE
--files-from=FILE read list of source-file names from FILE
-0, --from0 all *from/filter files are delimited by 0s
-s, --protect-args no space-splitting; wildcard chars only
--address=ADDRESS bind address for outgoing socket to daemon
--port=PORT specify double-colon alternate port number
--sockopts=OPTIONS specify custom TCP options
--blocking-io use blocking I/O for the remote shell
--stats give some file-transfer stats
-8, --8-bit-output leave high-bit chars unescaped in output
-h, --human-readable output numbers in a human-readable format
--progress show progress during transfer
-P same as --partial --progress
-i, --itemize-changes output a change-summary for all updates
--out-format=FORMAT output updates using the specified FORMAT
--log-file=FILE log what we're doing to the specified FILE
--log-file-format=FMT log updates using the specified FMT
--password-file=FILE read daemon-access password from FILE
--list-only list the files instead of copying them
--bwlimit=KBPS limit I/O bandwidth; KBytes per second
--write-batch=FILE write a batched update to FILE
--only-write-batch=FILE like --write-batch but w/o updating dest
--read-batch=FILE read a batched update from FILE
--protocol=NUM force an older protocol version to be used
--iconv=CONVERT_SPEC request charset conversion of filenames
--checksum-seed=NUM set block/file checksum seed (advanced)
-4, --ipv4 prefer IPv4
-6, --ipv6 prefer IPv6
--version print version number
(-h) --help show this help (see below for -h comment)
Добавить комментарий